Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) is one of the most important enzymes in human physiology, deficiencies in production or function of this enzyme have been associated with increased risk of different diseases [9, 1].
Quatrefolic®
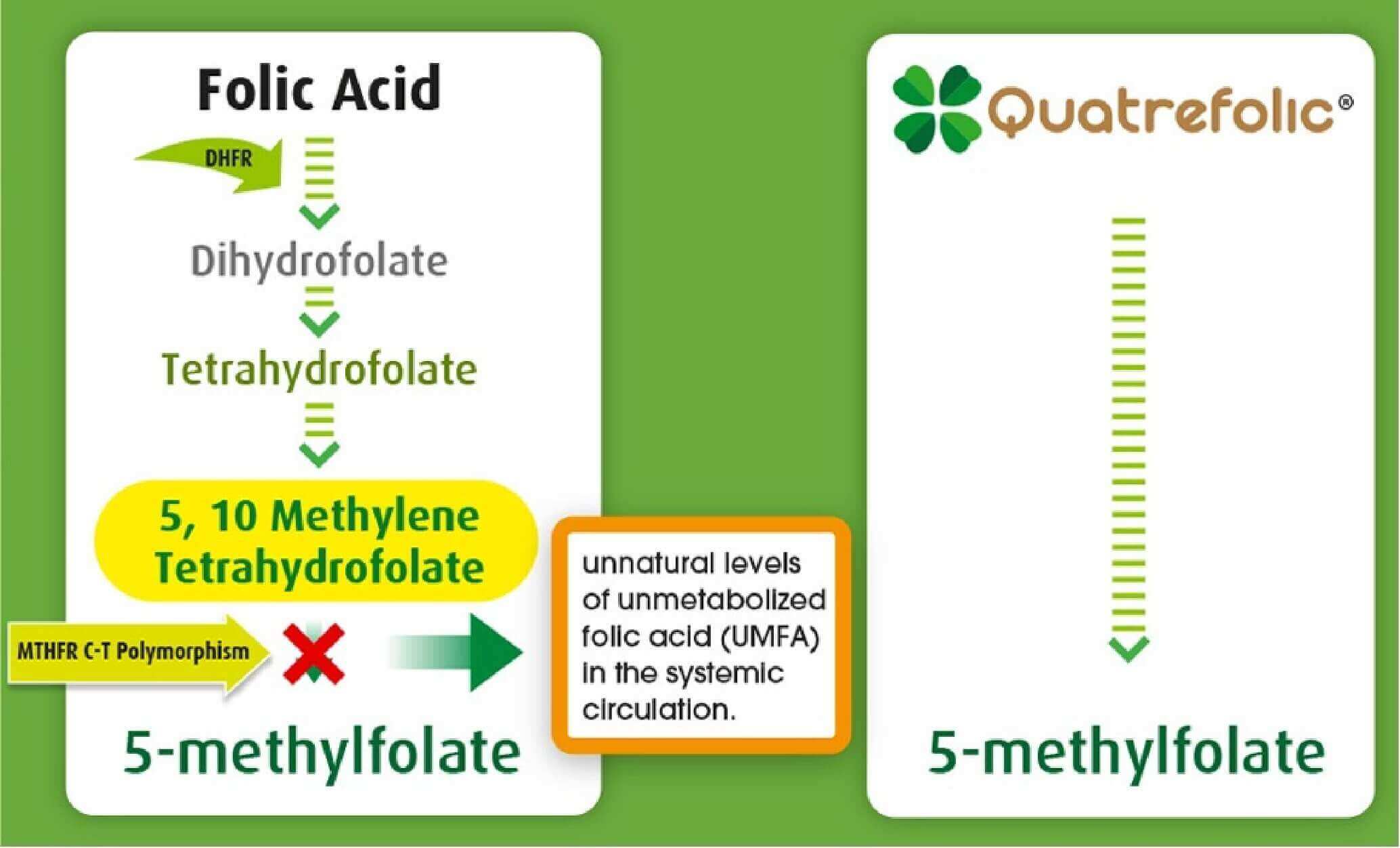
In the recent years increasing evidence of the advantages of reduced folate vs folic acid have been found. The rational use of reduced folate (particularly reduced and methylated such as Quatrefolic®) is derived from the inability of a part of world population to assimilate and metabolize folic acid from food or supplements (the most of folate assumption is coming from folic acid man-made version in supplements and added to foods).
Folic acid and also food folate are not biologically active and need to be converted to the metabolically active 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHF) through a multi steps process where the enzyme methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) owns a key role. Some individuals, due to their unique genetic patterns and expression, have polymorphic forms of this enzyme and do not produce adequate or effective MTHFR
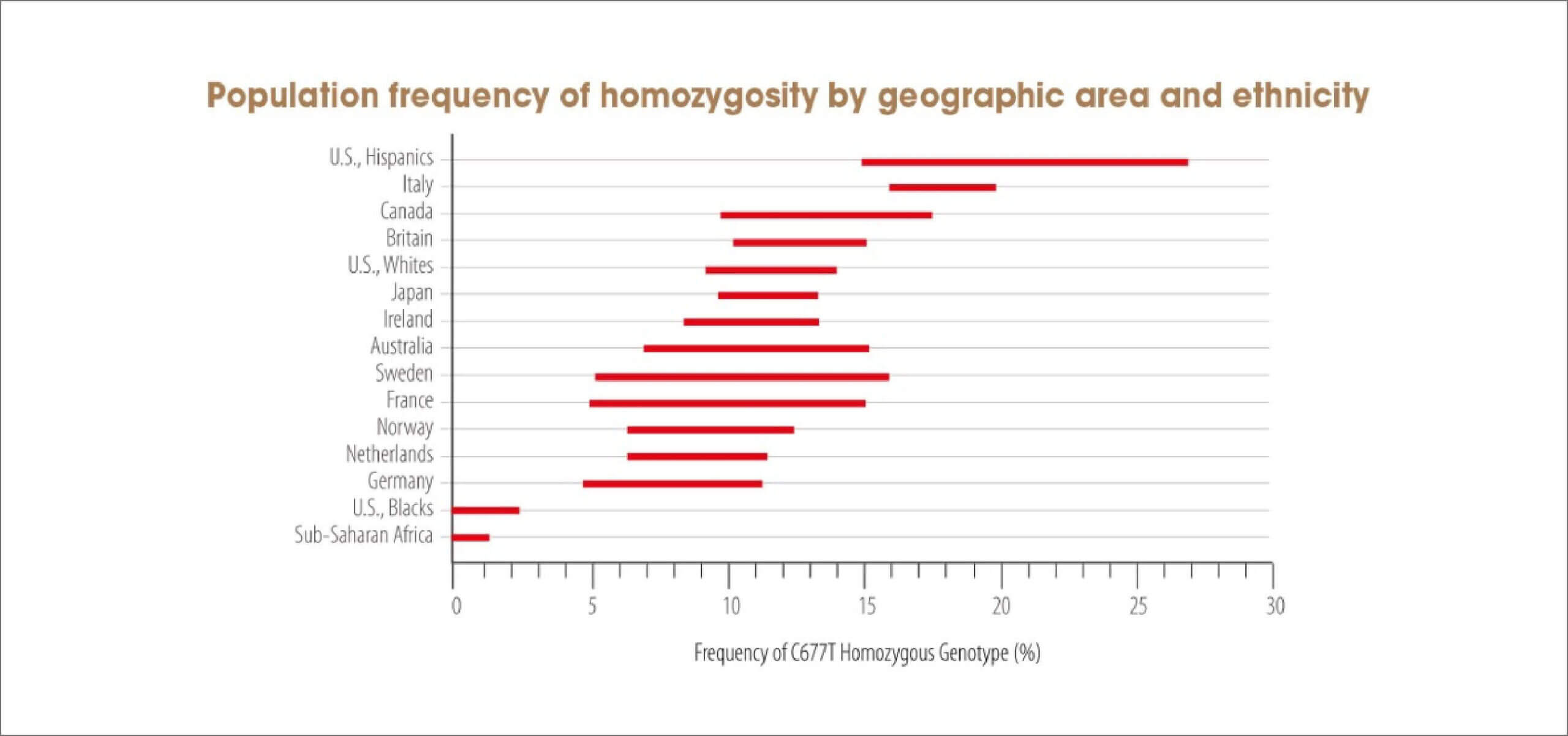
These defects related to MTHFR are very common, though they vary enormously between ethnic groups and regions [10, 11]. Emerging science of nutrigenomics indicates that MTHFR most often refers to a genetic mutation that inhibits the ability of the body to methylate (or convert folic acid from the food we eat into the metabolite we need, L-5-Methyltetrahydrofolate) so as some individuals cannot actually use folic acid [12]. Cutting-edge scientific research is shed light how much the MTHFR polymorphism is implicated in chronic disease states and how folate nutrition may contribute to replace adequate methylation and overall health [9]. The other advantage is that Quatrefolic® passes the gastric barrier and is absorbed mainly in the small intestine by a carrier mediated mechanism. The carrier is not saturated and this enables Quatrefolic® to ensure a higher folate uptake [1, 4].